Hi,
An example of line race.
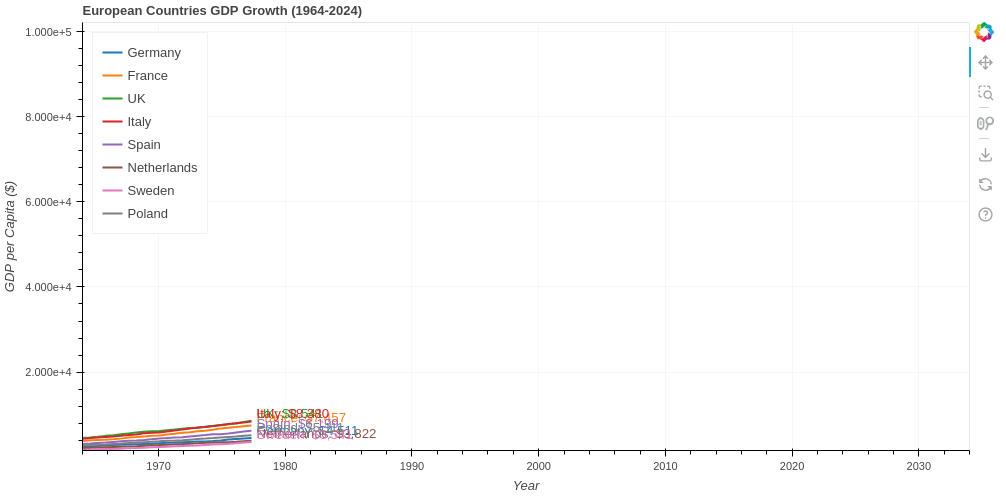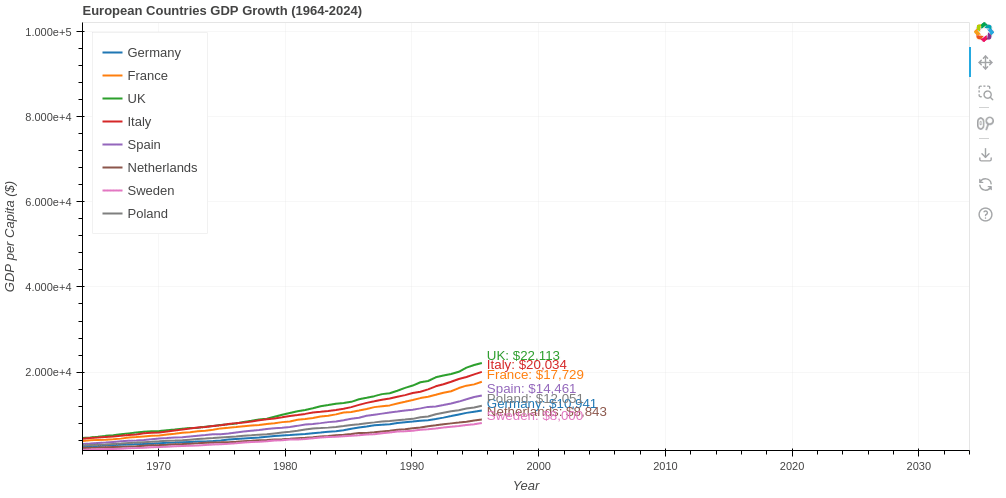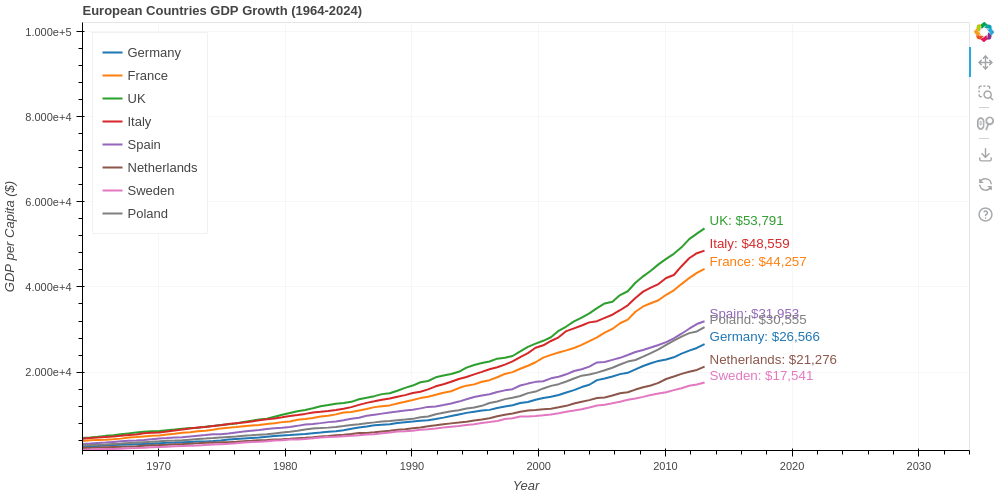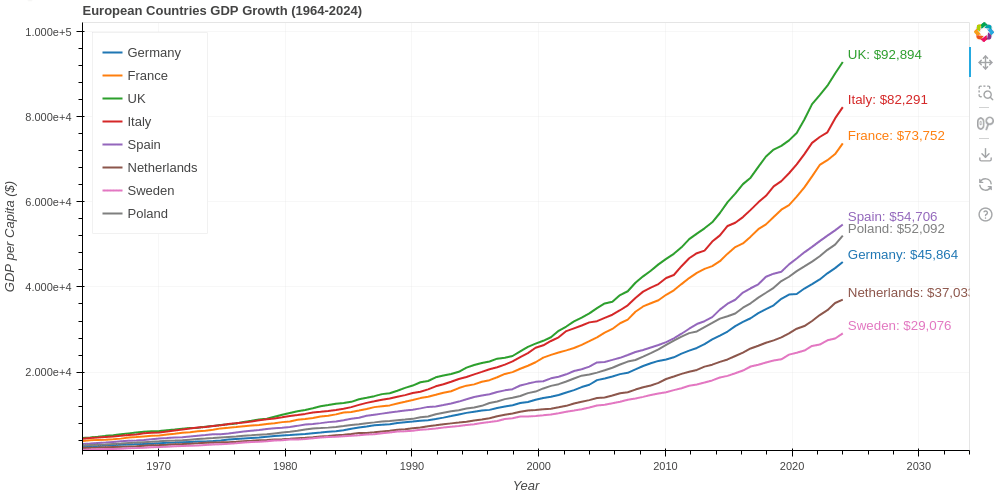
from bokeh.plotting import figure, curdoc
from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource, Label
import numpy as np
# Generate data for multiple countries
countries = ['Germany', 'France', 'UK', 'Italy', 'Spain', 'Netherlands', 'Sweden', 'Poland']
years = np.linspace(1964, 2024, 100)
data = {}
# Generate random growth curves for each country
np.random.seed(42)
for country in countries:
base = np.random.uniform(1000, 5000)
growth = np.random.normal(0.03, 0.01, len(years))
values = [base]
for rate in growth:
values.append(values[-1] * (1 + rate))
data[country] = np.array(values[:-1])
# Calculate max values for fixed axes
max_y = max(max(data[country]) for country in countries)
min_y = min(min(data[country]) for country in countries)
# Create initial data with first point
source = ColumnDataSource({
'x': [years[0]],
**{country: [data[country][0]] for country in countries}
})
# Create the plot
p = figure(title="European Countries GDP Growth (1964-2024)",
x_axis_label='Year', y_axis_label='GDP per Capita ($)',
width=1000, height=500,
x_range=(years[0], years[-1] + 10),
y_range=(min_y * 0.9, max_y * 1.1))
# Add lines and labels for each country
colors = ['#1f77b4', '#ff7f0e', '#2ca02c', '#d62728', '#9467bd', '#8c564b', '#e377c2', '#7f7f7f']
lines = {}
labels = {}
for country, color in zip(countries, colors):
# Add line
lines[country] = p.line('x', country, line_color=color, legend_label=country,
line_width=2, source=source)
# Add label
labels[country] = Label(
x=years[0], y=data[country][0],
text=f"{country}: ${int(data[country][0]):,}",
text_color=color,
text_font_size='10pt',
x_offset=5, y_offset=0
)
p.add_layout(labels[country])
# Style the plot
p.legend.click_policy = "hide"
p.legend.location = "top_left"
p.grid.grid_line_alpha = 0.3
# Animation counter
counter = 1
def animate():
global counter
if counter >= len(years):
return
# Update data
new_data = {
'x': years[:counter+1].tolist(),
**{country: data[country][:counter+1].tolist() for country in countries}
}
source.data = new_data
# Update labels
for country in countries:
current_value = data[country][counter]
labels[country].x = years[counter]
labels[country].y = current_value
labels[country].text = f"{country}: ${int(current_value):,}"
counter += 1
# Add periodic callback
doc = curdoc()
doc.add_periodic_callback(animate, 100) # 100ms between frames
doc.add_root(p)
bokeh serve --show app.py